Blog
What is a Topographic Map?
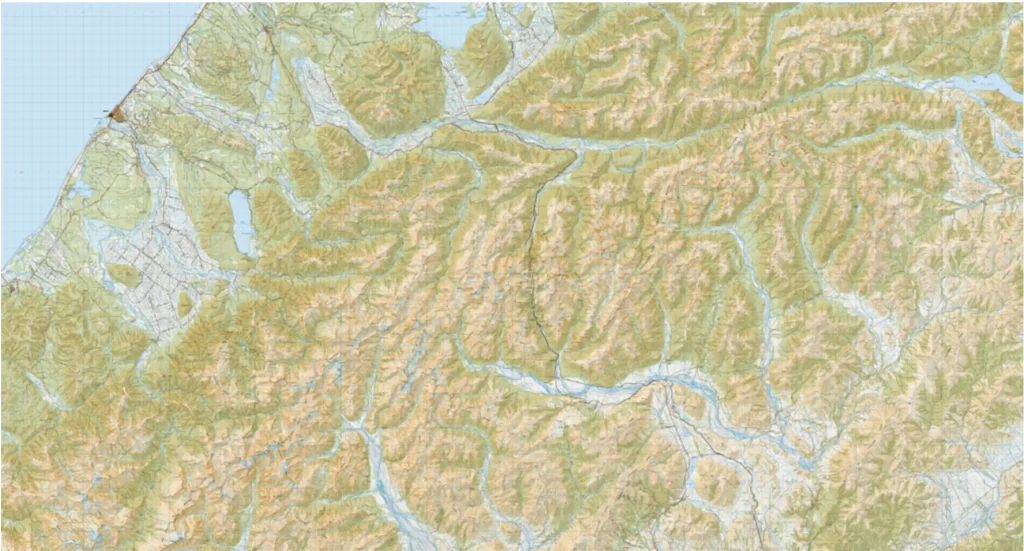
A topographic map is a detailed, graphic representation of the Earth’s surface, illustrating both natural and man-made features. Unlike simple maps that only show boundaries and roads, topographic maps depict the terrain and elevation through the use of contour lines, offering a three-dimensional perspective on a two-dimensional surface.
These maps are indispensable tools for various applications, from outdoor recreation and urban planning to environmental management and education.
Key Features of Topographic Maps
- Contour Lines: The hallmark of a topographic map is its contour lines, which connect points of equal elevation. These lines effectively represent the terrain’s shape, allowing users to visualize hills, valleys, slopes, and flat areas. The closer the contour lines are to each other, the steeper the terrain, while widely spaced lines indicate gentler slopes.
- Symbols and Colors: Topographic maps employ a variety of symbols and colors to represent different features. For example, blue typically denotes water bodies like rivers and lakes, green indicates forested areas, and brown is often used for contour lines. Man-made structures such as roads and buildings might be shown in black or red.
- Scale: The scale of a topographic map indicates the relationship between distances on the map and actual distances on the ground. Common scales include 1:24,000, where one unit on the map equals 24,000 units on the ground. The choice of scale depends on the map’s intended use, with larger scales providing more detail for smaller areas.
- Grids and Coordinates: These maps often include grid lines and coordinate systems like latitude and longitude, enabling precise location identification. The Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) system is another commonly used grid system on topographic maps.
Importance of Topographic Maps in New Zealand
New Zealand’s diverse and rugged terrain makes topographic maps particularly valuable for a variety of applications:
1.Outdoor Recreation: Topographic maps are essential for hikers, climbers, and outdoor enthusiasts. They provide detailed information on terrain, helping adventurers navigate safely through New Zealand’s varied landscapes, from coastal areas to mountainous regions. For example, the maps can indicate the steepness of a trail or the location of a river, allowing for better trip planning and risk assessment.
- Environmental Management: These maps are crucial for managing natural resources and planning conservation efforts. By providing detailed information on geographical features and ecosystems, topographic maps aid in understanding biodiversity and implementing sustainable environmental practices. They are also vital in disaster management, helping to identify flood-prone areas and plan evacuation routes.
- Urban Planning and Development: In urban planning, topographic maps help assess land suitability for development. They provide critical information on elevation, slope, and natural features, ensuring that infrastructure projects are designed with consideration for the terrain. This information is essential for minimizing environmental impact and enhancing the safety and sustainability of developments.
- Education and Research: In educational settings, topographic maps serve as valuable tools for teaching geography and earth sciences. They allow students to explore and understand the physical layout of the land, the relationship between different geographical features, and the impact of topography on human activities.
Using Topographic Maps in New Zealand
In New Zealand, topographic maps are widely accessible and used across various sectors. The government agency Land Information New Zealand (LINZ) provides a comprehensive series of topographic maps that cover the entire country. These maps are available both in print and digital formats, making them easily accessible for professionals and enthusiasts alike.
For outdoor enthusiasts, LINZ’s topographic maps are indispensable tools. They offer detailed information on hiking trails, camping sites, and other outdoor recreational activities. Maps like the NZTopo50 series, covering the entire country at a 1:50,000 scale, are particularly popular among hikers and climbers for their balance of detail and coverage.
Urban planners and developers rely on these maps to assess potential construction sites, design infrastructure projects, and ensure compliance with environmental regulations. The maps’ detailed depiction of terrain features helps planners understand the natural landscape and make informed decisions about land use.
Environmental scientists and conservationists use topographic maps to study ecosystems, monitor environmental changes, and plan conservation strategies. The maps help identify critical habitats, assess the impact of human activities, and develop plans to protect and restore natural areas.
Case Study: Topographic Maps in Environmental Conservation
One notable example of the use of topographic maps in New Zealand is in the conservation of the native kiwi bird. Conservationists use these maps to identify and protect kiwi habitats, plan pest control operations, and monitor the birds’ movements. By providing detailed information on the terrain, topographic maps enable conservationists to create effective management plans that consider the unique geographical features of kiwi habitats.
To conclude with:
Topographic maps are indispensable tools that provide a detailed view of the Earth’s surface, showcasing both natural and man-made features. In New Zealand, their importance spans outdoor recreation, environmental management, urban planning, and education. By accurately depicting terrain and elevation, topographic maps help individuals and organizations navigate and understand the complex landscapes of this beautiful country.
Whether you’re planning a hike in the Southern Alps, developing a new residential area, or working to conserve New Zealand’s unique ecosystems, topographic maps offer the detailed information needed to make informed decisions. Embracing the use of these maps can enhance our understanding of the land and contribute to more sustainable and enjoyable interactions with the environment.
Get yourself a Topographic Map